泛型编程相关理论学习
Variance
Variance describes how subtyping relationships between more complex types (e.g., generics, collections, or function types.) relate to subtyping relationships between their component types. It determines whether a type system allows substitutability in specific contexts, especially in generic programming.
- Invariance: The most restrictive relationship.
如果 A 是 B 的子类,但Container<A>和Container<B>没有任何关系。 - Covariance: Preserves the subtype relationship.
如果 A 是 B 的子类,则Container<A>是Container<B>的子类。 - Contravariance: Reverses the subtype relationship.
如果 A 是 B 的子类,则Container<A>是Container<B>的父类。
其中,Convariance和Contravariance与 OOP 中的多态性(Polymorphism)概念有密切联系。
具体可参考StackOverFlow中的回答以及 Eric Lippert 的系列文章
Invariance
Java 中的泛型具有不变性,无论 A 与 B 是否有继承关系,Container<A>和Container<B>都不会存在继承关系。
- Arrays differ from generic type in two important ways. First arrays are covariant. Generics are invariant.
- Covariant simply means if
Xis subtype ofYthenX[]will also be sub type ofY[]. Arrays are covariant As string is subtype of Object SoString[]is subtype ofObject[]- Invariant simply means irrespective of
Xbeing subtype ofYor not ,List<X>will not be subType ofList<Y>.《Effective Java》 Joshua Bloch
要验证这一点,可以考虑以下代码。如果ArrayList<Integer>是ArrayList<Number>的子类,那么以下代码应该是合法的。但实际上,编译器会报错。import java.util.ArrayList;public class Invariance { public static void main(String[] args) { // 获取 ArrayList 的 Class 对象 ArrayList<Number> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); list1 = list2; }}[ERROR] Type mismatch: cannot convert from ArrayList<Integer> to ArrayList<Number>Java(16777233) [Ln 8, Col 11]
A.isAssignableFrom(B)方法可以判断两个类之间是否存在继承关系,主要在 JDK 源码中使用
需要注意的是,由于类型擦除机制(Type Erasure),ArrayList<Integer> 和 ArrayList<Number> 在运行时
在运行时的类型都是 ArrayList,所以在运行时无法区分它们。通过以下代码判断两者的继承关系,会得到错误的结论import java.util.ArrayList;public class Invariance { public static void main(String[] args) { // 获取 ArrayList 的 Class 对象 ArrayList<Number> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList<>(); if (list1.getClass().isAssignableFrom(list2.getClass())) { System.out.println("list1 is assignable from list2"); } else { System.out.println("list1 is not assignable from list2"); } }}[OUTPUT] list1 is assignable from list2
Covariance
java 中的数组是协变的,考虑以下代码;String是Object的子类,所以String[]是Object[]的子类。String[] strings = new String[10];Object[] objects = strings;
JDK 开发人员在当时为什么要把数组设计成协变的而泛型为不可变的?感兴趣可以阅读https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18666710/why-are-arrays-covariant-but-generics-are-invariant
Contravariance
逆变性是协变性的反向操作。逆变性是指泛型的子类可以替代泛型的父类。
泛型设计成不变性有各方面的考量。但在理解起来可能有些别扭,苹果 IS A 水果,但装苹果的容器 IS NOT A 装水果的容器
为了更灵活且正确地使用泛型,可以考虑使用通配符(wildcard)。注意理解通配符的上下界限制,以及 PECS 原则。
Erausre
Releated Concepts
Reifiable type
A reifiable type is a type whose type information is fully available at runtime. This includes primitives, non-generic types, raw types, and invocations of unbound wildcards.
| examples | |
|---|---|
| Primitive types | int, double, boolean |
| None-generic | String, Integer |
| Raw types | List, Set |
| Unbound wildcard | List<?> |
Non-reifiable type
| examples | |
|---|---|
| parameterized types | List<String>, Map<Integer,String> |
| wildcard types | List<?>, List<? extends Number>, List<? super Integer> |
Tips: reifiable = reify(vt. 使具体化)+ able
Heap Pollution
Heap pollution in Java occurs when a variable of a parameterized type refers to an object that is not of that type.
Homogeneous/Heterogeneous translations
Java 架构师 Brian Goetz 在Background: How We Got the Generics We Have 中解释了泛型的设计理念,以及为什么选择了类型擦除机制。在这篇文章中,他提到了 translating parameterised types 的两种方案
- Homogeneous translation: a generic class
Foo<T>is translated into a single artifact, such asFoo.class(and same for generic methods)- Heterogeneous translation: each instantiation of a generic type or method (
Foo<String>, Foo<Integer>) is treated as a separate entity, and generates separate artifacts.Releated paper:《Two Ways to Bake Your Pizza— Translating Parameterised Types into Java》
Type Erasure in Java
Generics were introduced to the Java language to provide tighter type checks at compile time and to support generic programming. To implement generics, the Java compiler applies type erasure to:
- Replace all type parameters in generic types with their bounds or Object if the type parameters are unbounded.The produced bytecode, therefore, contains only ordinary classes, interfaces, and methods.
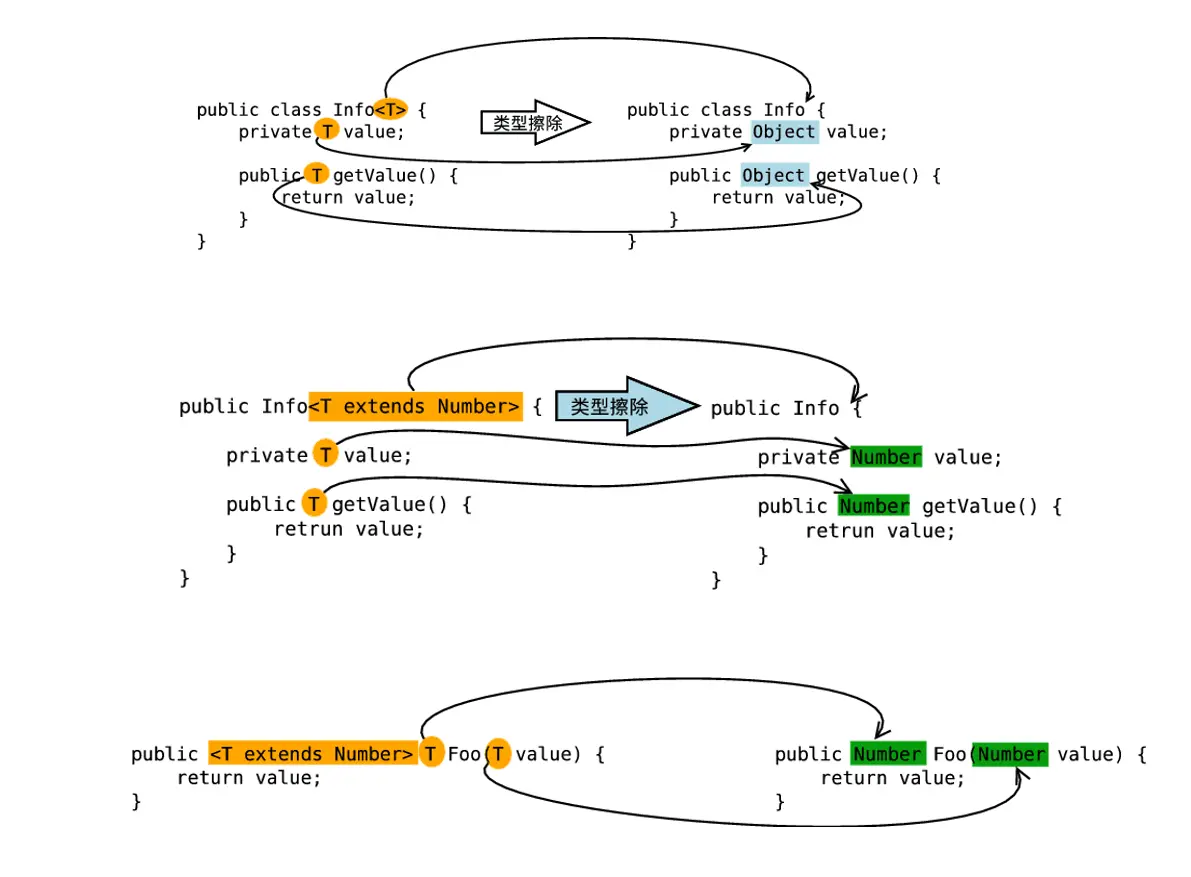
public class Box<T> { private T value; public void set(T value) { this.value = value; } public T get() { return value; }}public class Foo<T extends Number> { private T value; public void set(T value) { this.value = value; } public T get() { return value; }}public class Box { private Object value; public void set(Object value) { this.value = value; } public Object get() { return value; }}public class Foo { private Number value; public void set(Number value) { this.value = value; } public Number get() { return value; }}- Insert type casts if necessary to preserve type safety.
Box<Integer> integerBox = new Box<>();integerBox.set(10);Integer value = integerBox.get();Box integerBox = new Box();integerBox.set(10);Integer value = (Integer) integerBox.get(); // insert type cast- Generate bridge methods to preserve polymorphism in extended generic types.
Java 通过类型擦除确保了泛型的向后兼容性,但也可能导致方法签名的冲突,破坏多态性。桥接方法是一种由编译器生成的中间方法,目的是桥接父类和子类的方法实现,以保证多态性。class Parent<T> { public T getValue() { return null; }}// 泛型子类class Child extends Parent<String> { @Override public String getValue() { return "Child Value"; }}// Parent parent = new Child();// Object value = parent.getValue();// 调用链:// parent.getValue()// |// v// Child.bridge$getValue() // 桥接方法// |// v// Child.getValue() // 返回 String 类型的实际方法// |// v// "Child Value" (被转换为 Object 类型)public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Parent parent = new Child(); Object value = parent.getValue(); // JVM会调用桥接方法,再由桥接方法路由到子类方法 System.out.println(value); }}[OUTPUT] Child Value// 查看编译后的字节码$ javap -c Child[OUTPUT]class Child extends Parent<java.lang.String> { Child(); Code: 0: aload_0 1: invokespecial #1 // Method Parent."<init>":()V 4: return public java.lang.String getValue(); Code: 0: ldc #7 // String Child Value 2: areturn public java.lang.Object getValue(); Code: 0: aload_0 1: invokevirtual #9 // Method getValue:()Ljava/lang/String; 4: areturn}
Ref
docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/generics/erasure.html
docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/java/generics/nonReifiableVarargsType.html
An Expert‘s Guide to Generic Types in Java: Covariance, Contravariance, and Beyond
Java Generics - Bridge method? —— StackOverflow
Java bridge methods explained —— STAS
泛型编程相关理论学习